Table of Contents
Introduction
Imagine growing fresh, nutrient-rich vegetables and herbs year-round without a single handful of soil. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the reality of hydroponic systems, a revolutionary growing method that’s transforming how we think about agriculture and home gardening.
Hydroponic systems represent one of the most efficient and sustainable ways to grow plants, using up to 95% less water than traditional farming while producing yields that are 4-6 times higher. Whether you’re a complete beginner curious about soil-free growing or an experienced gardener looking to optimize your harvest, understanding how hydroponic systems work is your first step toward joining the millions of growers worldwide who have embraced this innovative technology.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about hydroponic systems—from the basic science behind how they work to the different types available and how you can get started with your own hydroponic garden today.
What Are Hydroponic Systems?
The Scientific Definition
Hydroponic systems are soil-free growing methods that deliver nutrients directly to plant roots through water-based solutions. The term “hydroponics” comes from the Greek words “hydro” (water) and “ponos” (labor), literally meaning “water working.” Instead of relying on soil to provide nutrients, hydroponic systems use carefully balanced nutrient solutions that give plants exactly what they need, when they need it.
This precise control over nutrition, combined with optimal environmental conditions, allows plants to focus their energy on growth rather than searching for nutrients in soil. The result? Faster growth rates, higher yields, and healthier plants that can be grown in virtually any location with the right setup.
Key Components of Hydroponic Systems
Every hydroponic system, regardless of its complexity, relies on several fundamental components working together:
1. Growing Medium
Unlike soil, hydroponic growing media provide physical support for plants while allowing excellent drainage and aeration. Common options include:
- Rockwool: Sterile, pH-neutral fibers that retain moisture while providing excellent drainage
- Clay pebbles: Lightweight, reusable spheres that promote root aeration
- Perlite: Volcanic glass that’s lightweight and provides excellent drainage
- Coconut coir: Sustainable fiber that retains moisture while allowing air flow
2. Nutrient Solution
This is the lifeblood of any hydroponic system—a carefully balanced mixture of water and essential nutrients that plants need to thrive. The solution typically contains:
- Macronutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K)
- Secondary nutrients: Calcium, Magnesium, and Sulfur
- Micronutrients: Iron, Manganese, Zinc, and other trace elements
3. Water Delivery System
This includes pumps, tubes, and reservoirs that circulate the nutrient solution to plant roots. The delivery method varies by system type but always ensures plants receive consistent nutrition and hydration.
4. Environmental Controls
Modern hydroponic systems often include monitoring and control systems for:
- pH levels (typically 5.5-6.5 for most plants)
- Electrical conductivity (EC) to measure nutrient concentration
- Temperature control for both air and nutrient solution
- Lighting systems for indoor growing

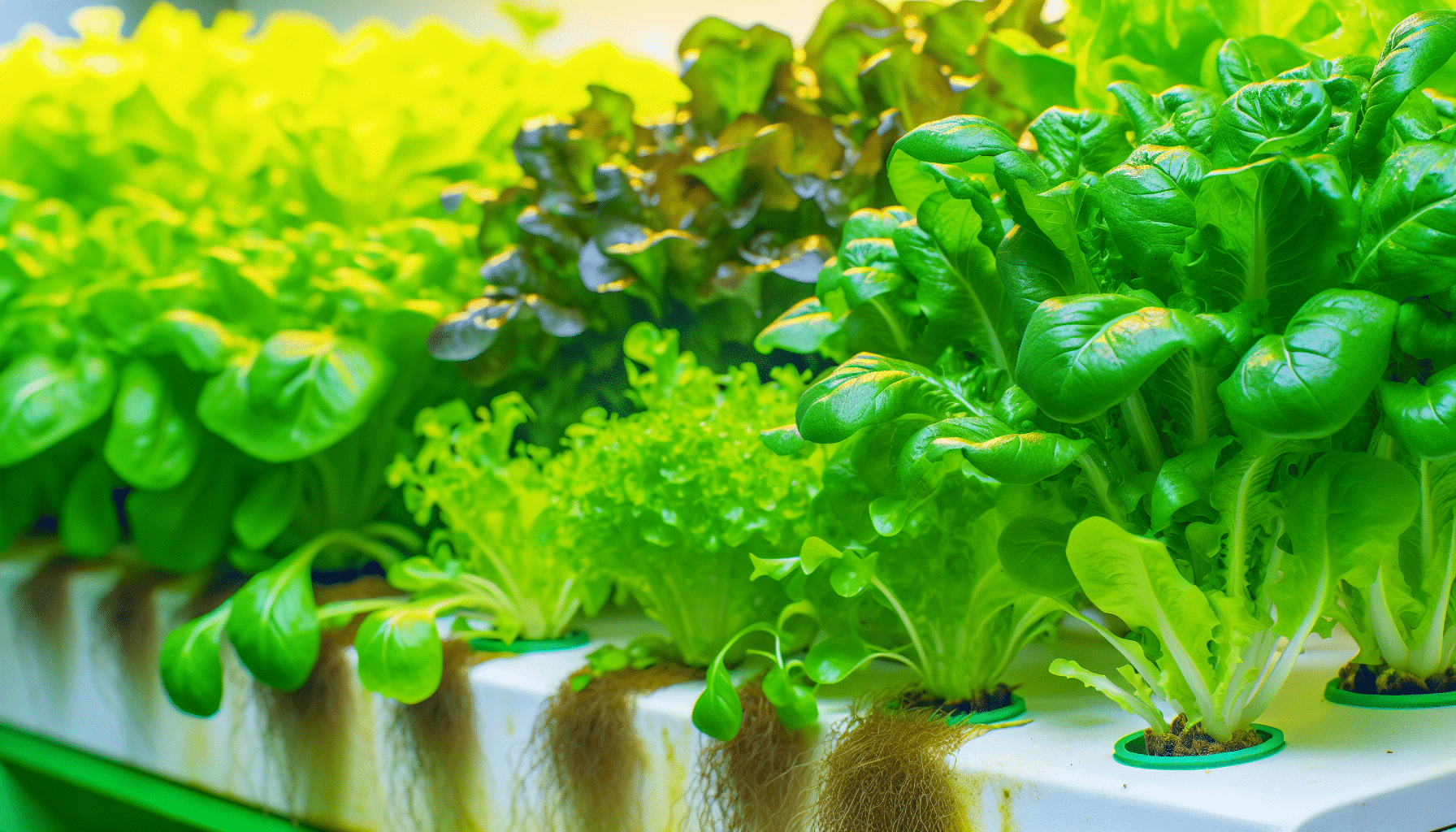
Hydroponic systems offer significant advantages over traditional soil-based growing methods
Soil vs. Soilless Growing: Understanding the Difference
Traditional soil-based gardening relies on complex ecosystems where plants must compete for nutrients, water, and space. Soil quality varies dramatically, and plants often struggle with issues like:
- Nutrient deficiencies or imbalances
- Poor drainage leading to root rot
- Soil-borne pests and diseases
- Inconsistent water availability
- Limited growing seasons
Hydroponic systems eliminate these variables by providing:
- Precise nutrition: Plants receive exactly the nutrients they need in optimal ratios
- Consistent water supply: No drought stress or waterlogging
- Disease prevention: Sterile growing environments reduce pest and disease pressure
- Year-round growing: Climate-controlled environments enable continuous production
- Space efficiency: Vertical growing and higher plant density maximize yields
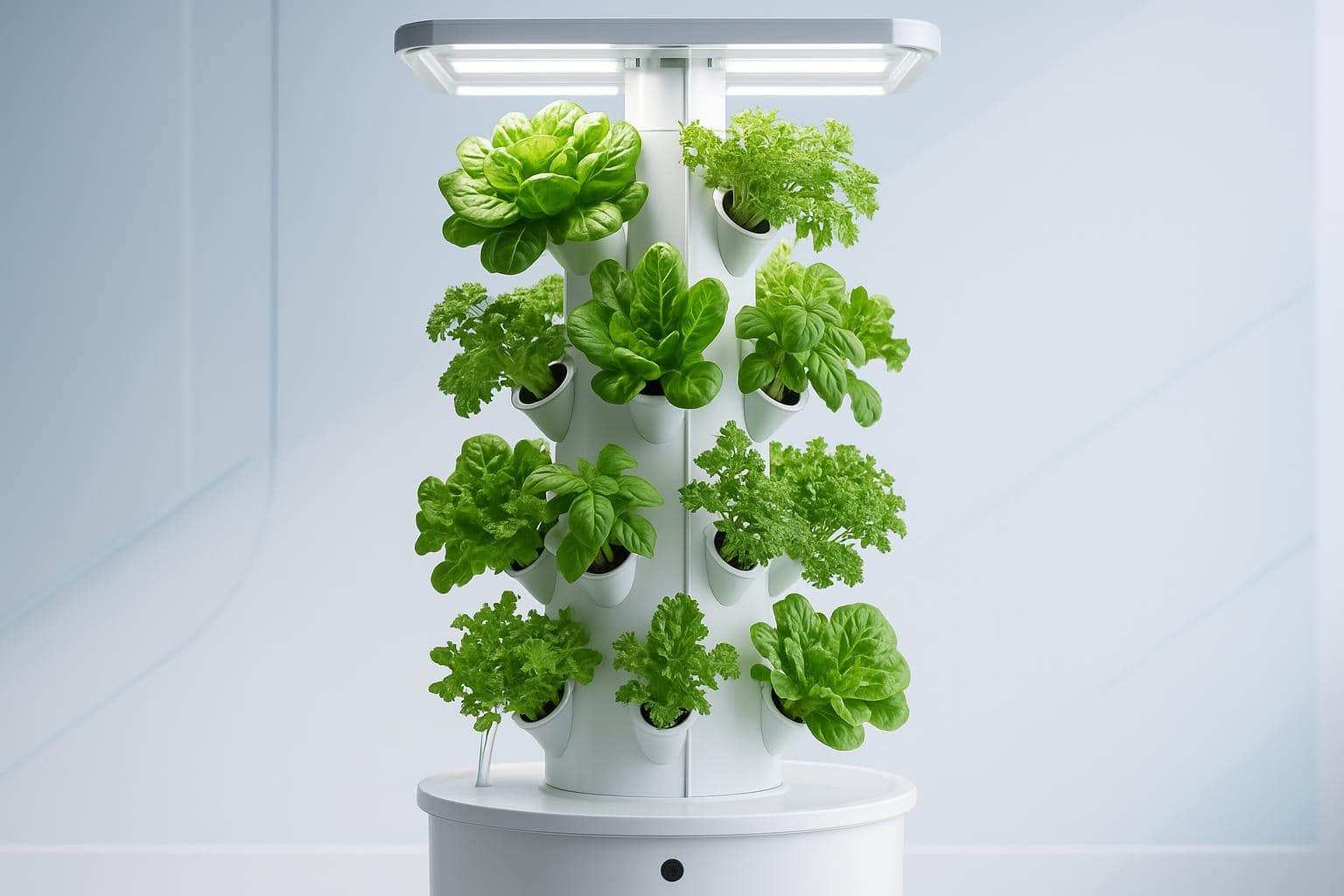
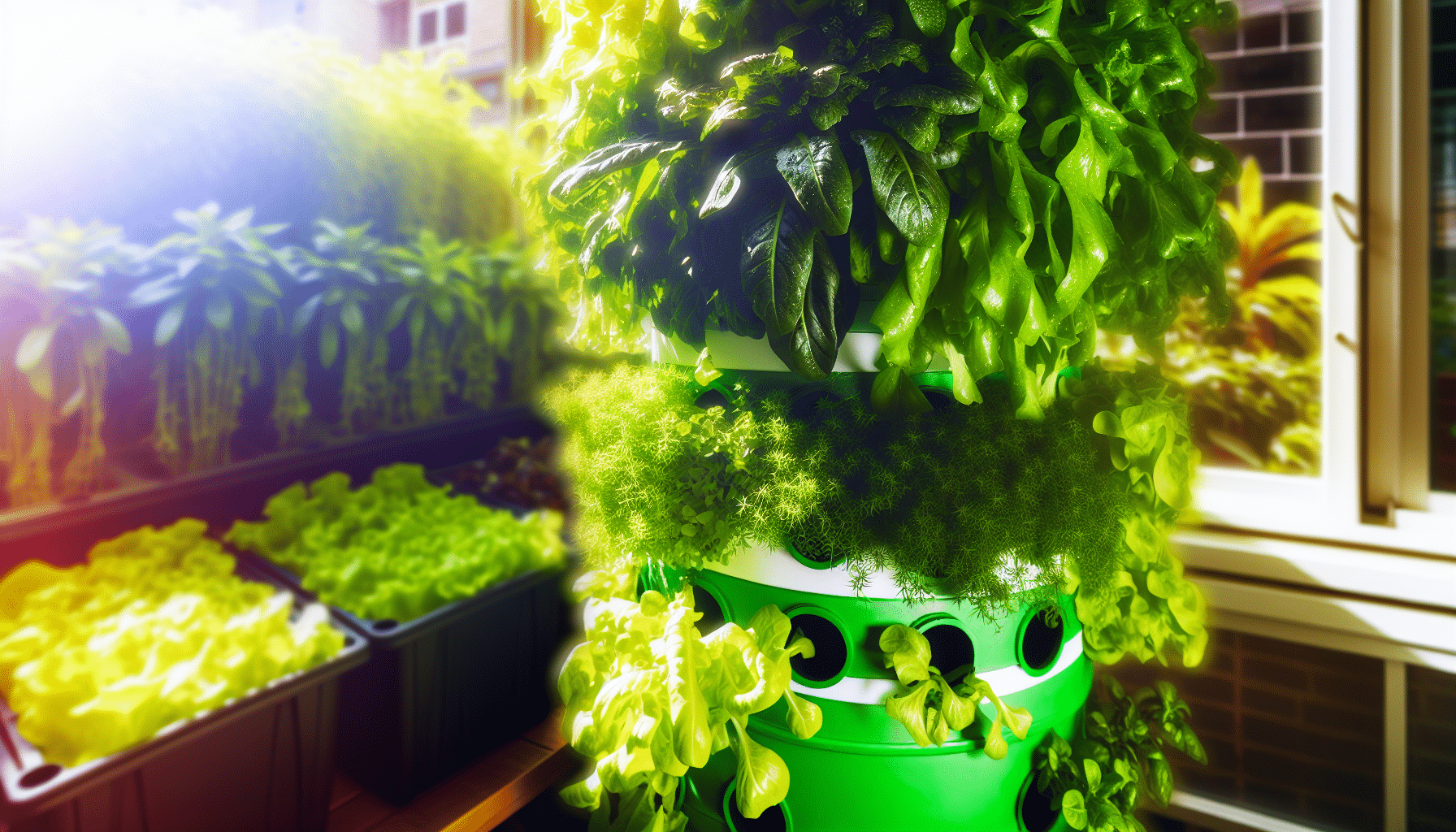
How Hydroponic Systems Work

The hydroponic process: from nutrient reservoir to optimal plant growth
The Nutrient Delivery Mechanism
The heart of any hydroponic system is its ability to deliver nutrients directly to plant roots in a form they can immediately absorb. Here’s how this process works:
1. Nutrient Preparation
Concentrated nutrient solutions are mixed with water to create the perfect feeding solution for plants. This mixture is carefully balanced to provide:
- The right pH level for optimal nutrient uptake
- Proper electrical conductivity indicating nutrient concentration
- Essential macro and micronutrients in bioavailable forms
2. Root Zone Delivery
Unlike soil-grown plants that must search for nutrients, hydroponic plants have nutrients delivered directly to their root zone through various methods:
- Continuous flow: Nutrient solution flows constantly past roots
- Flood and drain: Periodic flooding of the root zone followed by drainage
- Drip irrigation: Slow, steady dripping of nutrients to individual plants
- Misting: Fine spray of nutrients directly onto exposed roots
3. Nutrient Uptake
Plant roots absorb nutrients and water directly from the solution, allowing for:
- Faster nutrient uptake compared to soil-based systems
- More efficient use of nutrients with minimal waste
- Immediate response to changing nutritional needs
Water Circulation and Oxygenation
Proper water circulation is crucial for hydroponic success, serving multiple vital functions:
Circulation Benefits:
- Even distribution: Ensures all plants receive equal nutrition
- Temperature regulation: Prevents hot spots and maintains optimal root temperature
- Waste removal: Carries away plant waste products and excess salts
- Fresh nutrient delivery: Constantly replenishes nutrients around roots
Oxygenation Process:
Plant roots need oxygen to function properly, and hydroponic systems provide this through:
- Air pumps and stones: Bubble air through nutrient solutions
- Venturi valves: Use water flow to draw air into the system
- Waterfall effects: Create turbulence that naturally oxygenates water
- Ebb and flow cycles: Allow air to reach roots during drain periods
Environmental Control Systems
Modern hydroponic systems excel because they provide precise environmental control:
pH Management:
- Automated pH monitoring and adjustment systems
- Buffer solutions to maintain stable pH levels
- Regular testing and calibration for optimal nutrient uptake
Temperature Control:
- Nutrient solution chillers for hot climates
- Heating elements for cold environments
- Air circulation systems for consistent temperatures
Lighting Systems:
- Full-spectrum LED grow lights that mimic natural sunlight
- Programmable timers for optimal photoperiods
- Energy-efficient lighting that produces minimal heat
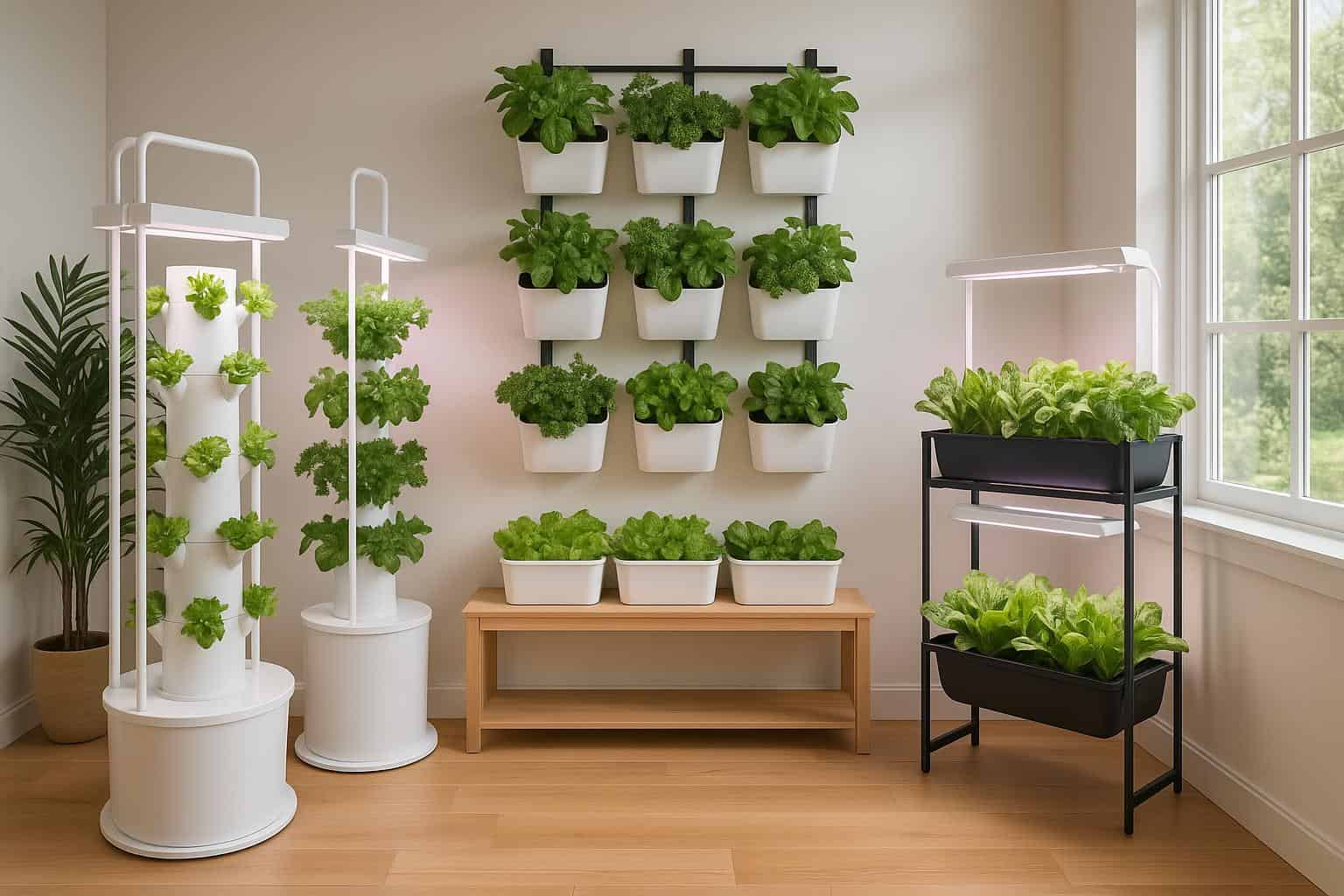
Types of Hydroponic Systems

The five main types of hydroponic systems, each with unique advantages
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture is one of the simplest and most popular hydroponic methods, especially for beginners.
How it Works:
Plants are suspended in net pots filled with growing medium, with their roots dangling directly into oxygenated nutrient solution. Air pumps continuously bubble air through the solution, providing essential oxygen to the roots.
Best For:
- Leafy greens (lettuce, spinach, kale)
- Herbs (basil, cilantro, mint)
- Fast-growing plants with smaller root systems
Advantages:
- Simple setup and maintenance
- Low cost to start
- Excellent growth rates for suitable plants
- Easy to monitor and adjust nutrients
Considerations:
- Requires constant power for air pumps
- Limited to smaller plants
- Vulnerable to power outages
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT systems create a thin film of nutrient solution that flows continuously past plant roots, providing both nutrition and oxygenation.
How it Works:
Plants are placed in sloped channels where a thin film of nutrient solution flows from a reservoir, past the roots, and back to the reservoir. The constant flow ensures fresh nutrients while the thin film allows roots to access oxygen from the air.
Best For:
- Leafy greens and herbs
- Strawberries
- Small to medium-sized plants
Advantages:
- Water and nutrient efficient
- Good oxygenation of roots
- Easy to scale up or down
- Minimal growing medium required
Considerations:
- Vulnerable to pump failures
- Can develop algae in channels
- Requires proper slope for drainage
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
This system periodically floods the growing area with nutrient solution, then drains it back to the reservoir.
How it Works:
A timer controls a pump that floods the growing bed with nutrient solution. After a set period, the pump turns off and the solution drains back to the reservoir through an overflow tube. This cycle repeats several times per day.
Best For:
- Wide variety of plants
- Larger plants with extensive root systems
- Mixed plantings with different nutritional needs
Advantages:
- Versatile for many plant types
- Good root oxygenation during drain cycles
- Relatively simple and reliable
- Can use various growing media
Considerations:
- Requires timer reliability
- Potential for pump failures
- Needs proper drainage design
Drip Systems
Drip systems deliver nutrient solution directly to individual plants through small tubes and emitters.
How it Works:
A pump delivers nutrient solution from a reservoir through a network of tubes to drip emitters placed near each plant. The solution can either drain back to the reservoir (recovery system) or drain away (non-recovery system).
Best For:
- Larger plants (tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers)
- Plants with varying nutritional needs
- Commercial growing operations
Advantages:
- Precise control over individual plant nutrition
- Water and nutrient efficient
- Scalable for large operations
- Works well with various growing media
Considerations:
- More complex setup
- Emitters can clog
- Requires regular maintenance
Aeroponic Systems
Aeroponics represents the most advanced form of hydroponic growing, where plant roots are suspended in air and misted with nutrient solution.
How it Works:
Plants are held in net pots or foam inserts with their roots hanging freely in an enclosed chamber. High-pressure pumps create a fine mist of nutrient solution that’s sprayed directly onto the roots at regular intervals.
Best For:
- Fast-growing leafy greens
- Herbs and microgreens
- Propagation and cloning
- Research and experimental growing
Advantages:
- Maximum oxygen exposure for roots
- Fastest growth rates
- Most efficient nutrient and water use
- Easy root inspection and harvesting
Considerations:
- Most complex and expensive system
- Requires reliable misting equipment
- Vulnerable to equipment failures
- Needs sterile conditions
Benefits of Hydroponic Systems

Key benefits that make hydroponic systems superior to traditional growing methods
Faster Growth Rates and Higher Yields
One of the most compelling advantages of hydroponic systems is their ability to dramatically accelerate plant growth and increase yields:
Growth Rate Improvements:
- Lettuce: 30-50% faster growth compared to soil
- Herbs: 25-40% faster maturation
- Tomatoes: 20-30% faster fruit development
- Leafy greens: Harvest cycles reduced from 45-60 days to 28-35 days
Yield Increases:
- 4-6 times higher yields per square foot
- Multiple harvests per year instead of seasonal growing
- Higher plant density through vertical growing
- Consistent production regardless of weather
Why Hydroponics Grows Faster:
- Direct nutrient access: No energy wasted searching for nutrients
- Optimal nutrition: Perfect nutrient ratios for each growth stage
- Consistent conditions: No stress from drought, flooding, or temperature extremes
- Enhanced oxygenation: Better root health leads to faster growth
Water Efficiency and Conservation
Despite being water-based, hydroponic systems are incredibly water-efficient:
Water Savings:
- 90-95% less water usage compared to traditional farming
- Closed-loop systems recycle and reuse water
- No water loss to soil absorption or runoff
- Precise delivery eliminates waste
Conservation Methods:
- Recirculating systems: Water is continuously reused
- Targeted delivery: Water goes directly to roots, not surrounding soil
- Evaporation control: Covered reservoirs minimize water loss
- Smart monitoring: Sensors prevent overwatering
Year-Round Growing Capability
Hydroponic systems enable continuous production regardless of season or climate:
Climate Independence:
- Indoor growing eliminates weather dependency
- Controlled environments maintain optimal conditions
- No seasonal limitations on crop selection
- Protection from extreme weather events
Continuous Harvests:
- Staggered planting for ongoing production
- Multiple crops per year instead of single seasons
- Fresh produce available 365 days per year
- Consistent quality and availability
Pest and Disease Control
Hydroponic systems provide natural advantages for pest and disease management:
Disease Prevention:
- Sterile growing media eliminate soil-borne pathogens
- Controlled environments reduce disease pressure
- Easy sanitation between growing cycles
- No contaminated soil to spread problems
Pest Management:
- Physical barriers easier to implement
- Beneficial insects more effective in controlled environments
- Reduced pesticide needs
- Early detection and intervention possible
Space Efficiency and Urban Growing
Hydroponic systems maximize growing potential in limited spaces:
Vertical Growing:
- Multi-level systems increase growing area
- Tower gardens utilize vertical space efficiently
- Suitable for apartments, balconies, and small yards
- Urban agriculture becomes viable
Higher Plant Density:
- Closer plant spacing without competition for nutrients
- No need for wide rows for cultivation equipment
- Efficient use of available space
- Suitable for indoor growing
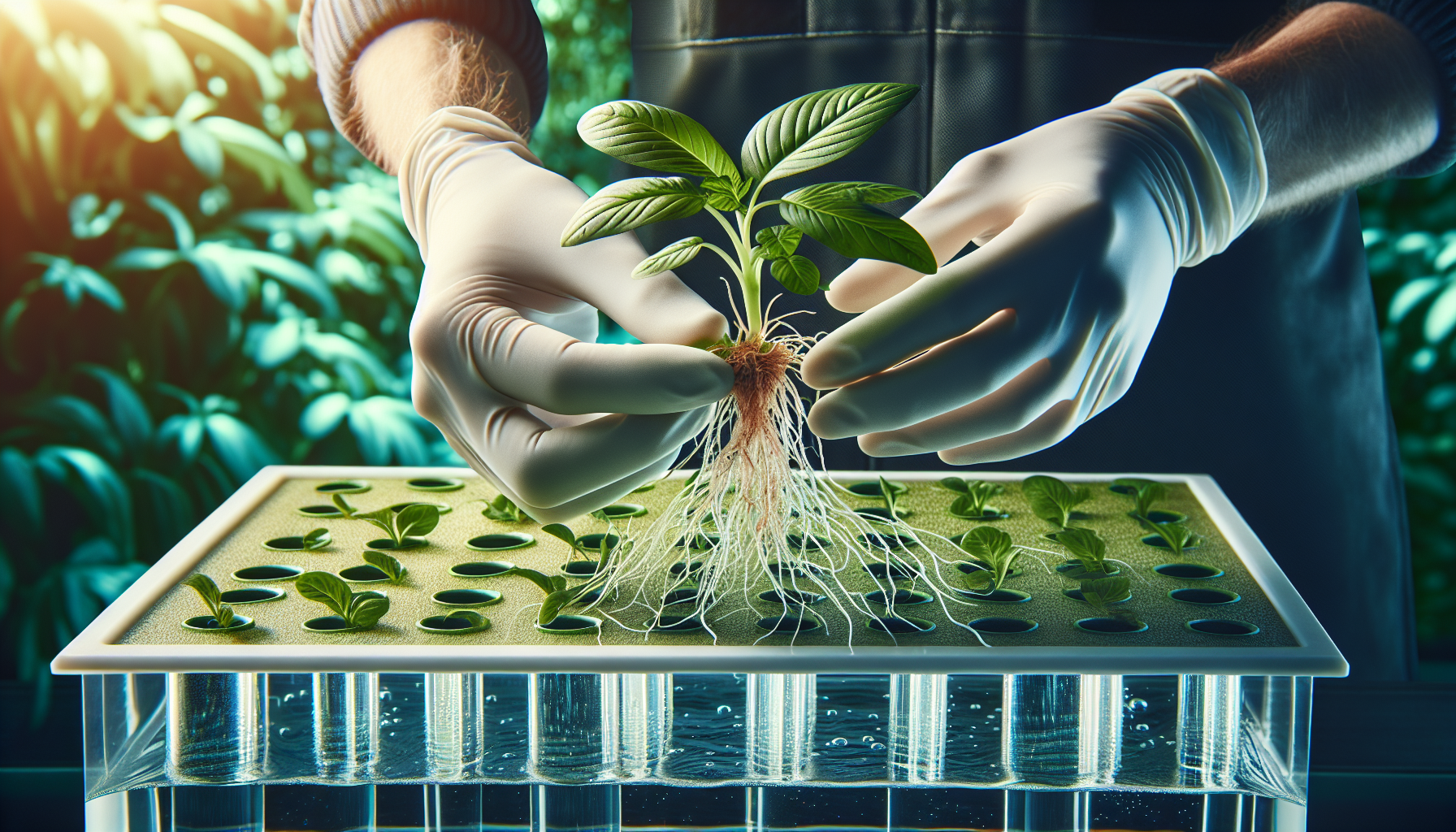
Getting Started with Hydroponic Systems

Your step-by-step guide to setting up your first hydroponic system
Choosing Your First System
For beginners, selecting the right hydroponic system is crucial for success. Consider these factors:
Beginner-Friendly Options:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Simple, affordable, and forgiving
- Kratky Method: Passive system requiring no electricity
- Small NFT systems: Good introduction to flowing systems
- All-in-one units: Complete systems with everything included
Factors to Consider:
- Available space: Indoor vs. outdoor, size limitations
- Budget: Initial investment and ongoing costs
- Time commitment: Daily maintenance requirements
- Plant preferences: What you want to grow
- Technical comfort: Your comfort with equipment and monitoring
Essential Equipment for Beginners
Starting your hydroponic journey requires some basic equipment:
Core Components:
- Growing system: Choose based on your space and goals
- Growing medium: Rockwool, clay pebbles, or coconut coir
- Nutrients: Complete hydroponic nutrient solutions
- pH testing kit: Essential for monitoring water chemistry
- Growing containers: Net pots, growing trays, or towers
Monitoring Tools:
- pH meter: Digital meters provide accurate readings
- EC/TDS meter: Measures nutrient concentration
- Thermometer: Monitor air and water temperature
- Timer: Automate lighting and watering cycles
Lighting (for indoor growing):
- LED grow lights: Energy-efficient full-spectrum lighting
- Timer controls: Automate light cycles
- Reflectors: Maximize light efficiency
- Light meters: Ensure adequate light levels
Best Plants for Hydroponic Beginners
Start with easy-to-grow plants that are forgiving and fast-growing:
Excellent Beginner Plants:
- Lettuce: Fast-growing, tolerates mistakes, multiple varieties
- Spinach: Hardy, nutritious, grows in cooler conditions
- Basil: Aromatic, fast-growing, high value crop
- Mint: Nearly indestructible, spreads quickly
- Cilantro: Fast-growing, multiple harvests possible
Good Second-Step Plants:
- Kale: Nutritious, tolerates temperature variations
- Swiss chard: Colorful, productive, long harvest period
- Arugula: Spicy greens, fast-growing, cool weather crop
- Green onions: Easy to grow, continuous harvest
- Microgreens: Quick turnaround, high value, minimal space
Plants to Avoid Initially:
- Large fruiting plants (tomatoes, peppers) – require more advanced systems
- Root vegetables – need deep growing media
- Plants with specific pH requirements
- Slow-growing plants that tie up space
Setting Up Your First System
Follow these steps for a successful start:
1. Choose Your Location
- Adequate light (natural or artificial)
- Stable temperature (65-75°F ideal)
- Access to electricity and water
- Good ventilation
- Level surface for equipment
2. Assemble Your System
- Follow manufacturer instructions carefully
- Test all pumps and timers before adding plants
- Ensure proper drainage and overflow protection
- Check for leaks with plain water first
3. Prepare Your Nutrient Solution
- Use quality hydroponic nutrients
- Follow mixing instructions precisely
- Test and adjust pH to 5.5-6.5
- Check EC/TDS levels for proper concentration
4. Plant Your First Crop
- Start with seedlings rather than seeds
- Use appropriate growing medium
- Ensure proper spacing for mature plant size
- Label plants with variety and planting date
5. Monitor and Maintain
- Check pH and nutrient levels daily initially
- Monitor plant health and growth
- Maintain proper water levels
- Keep detailed records of what works
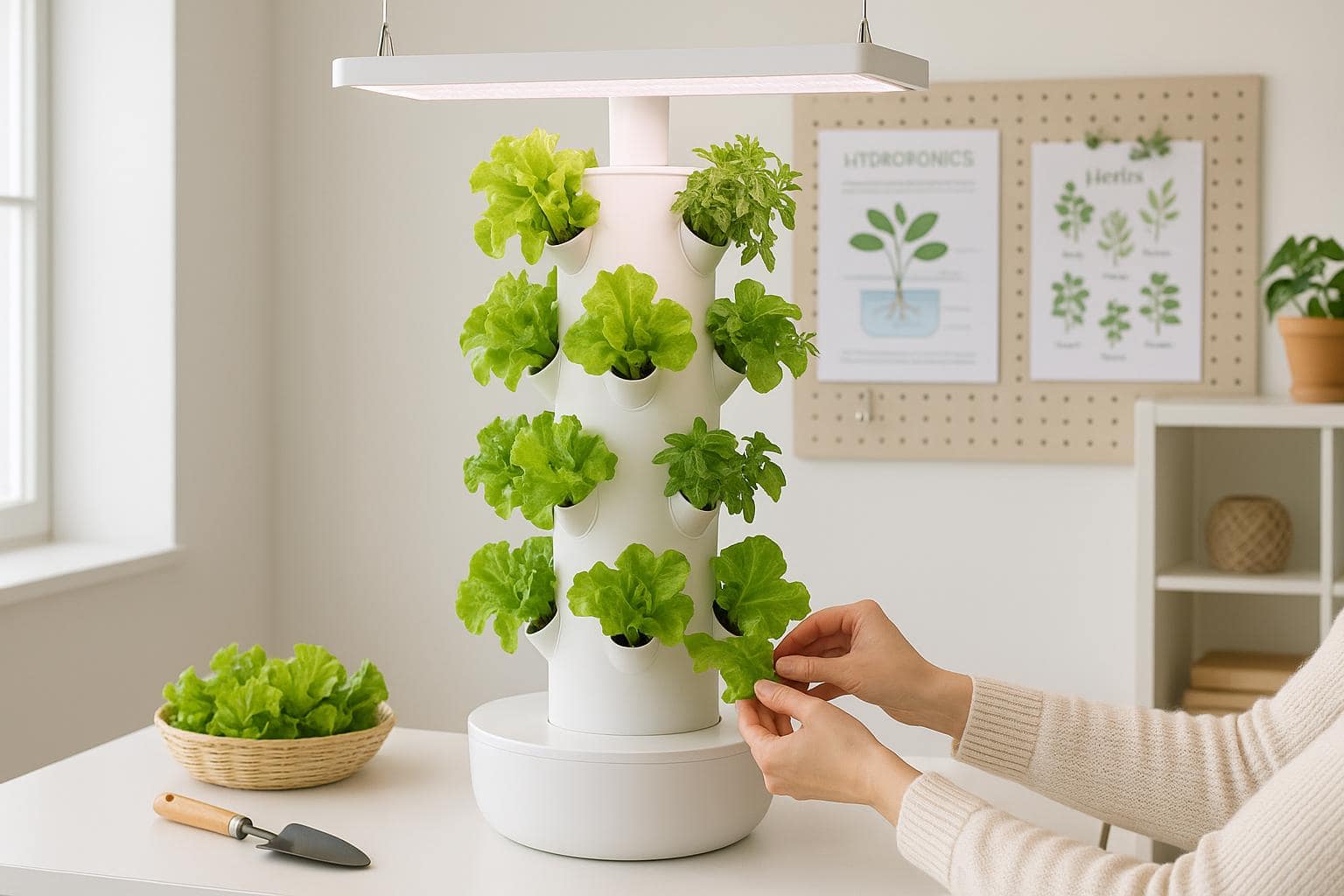
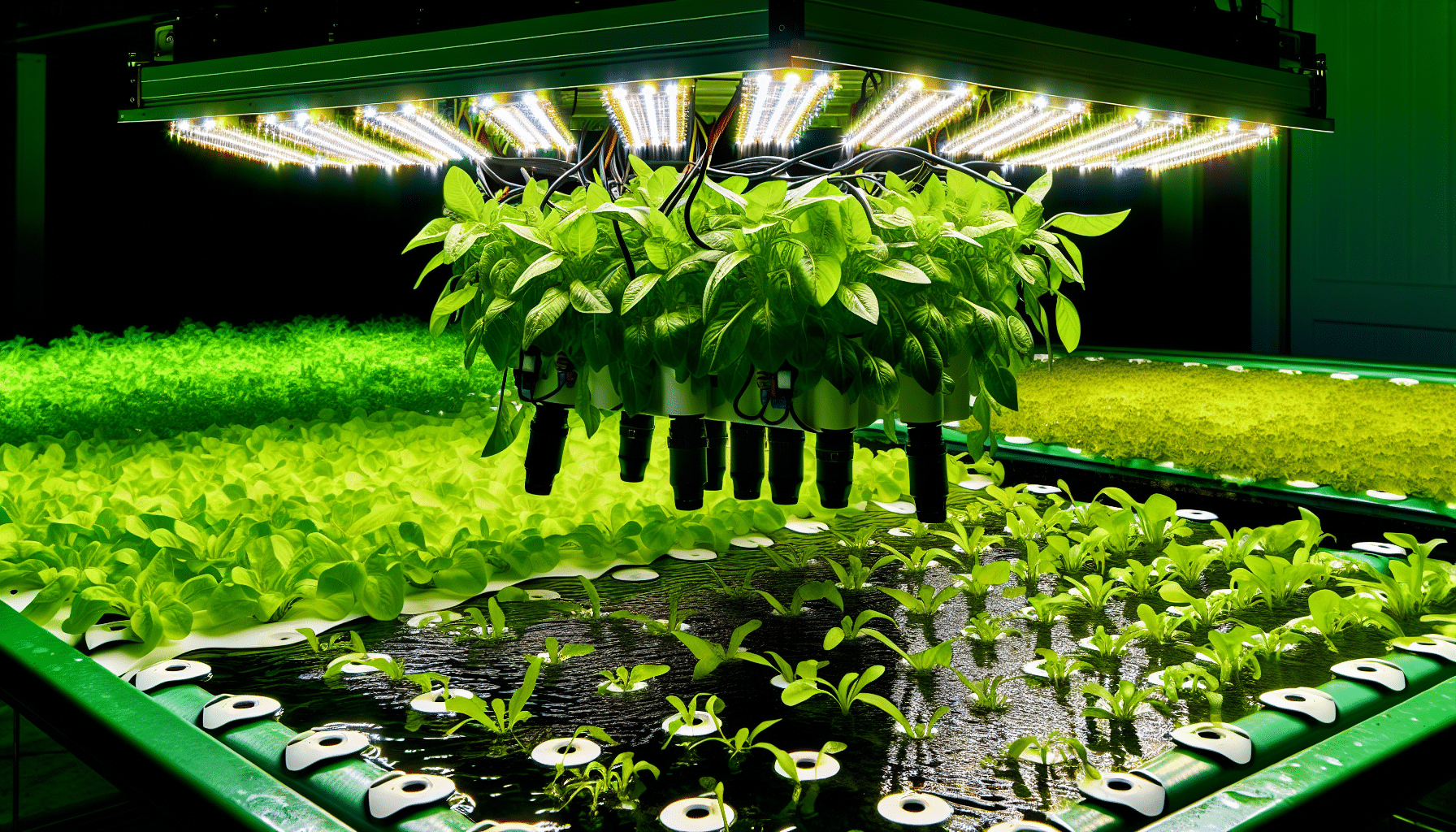
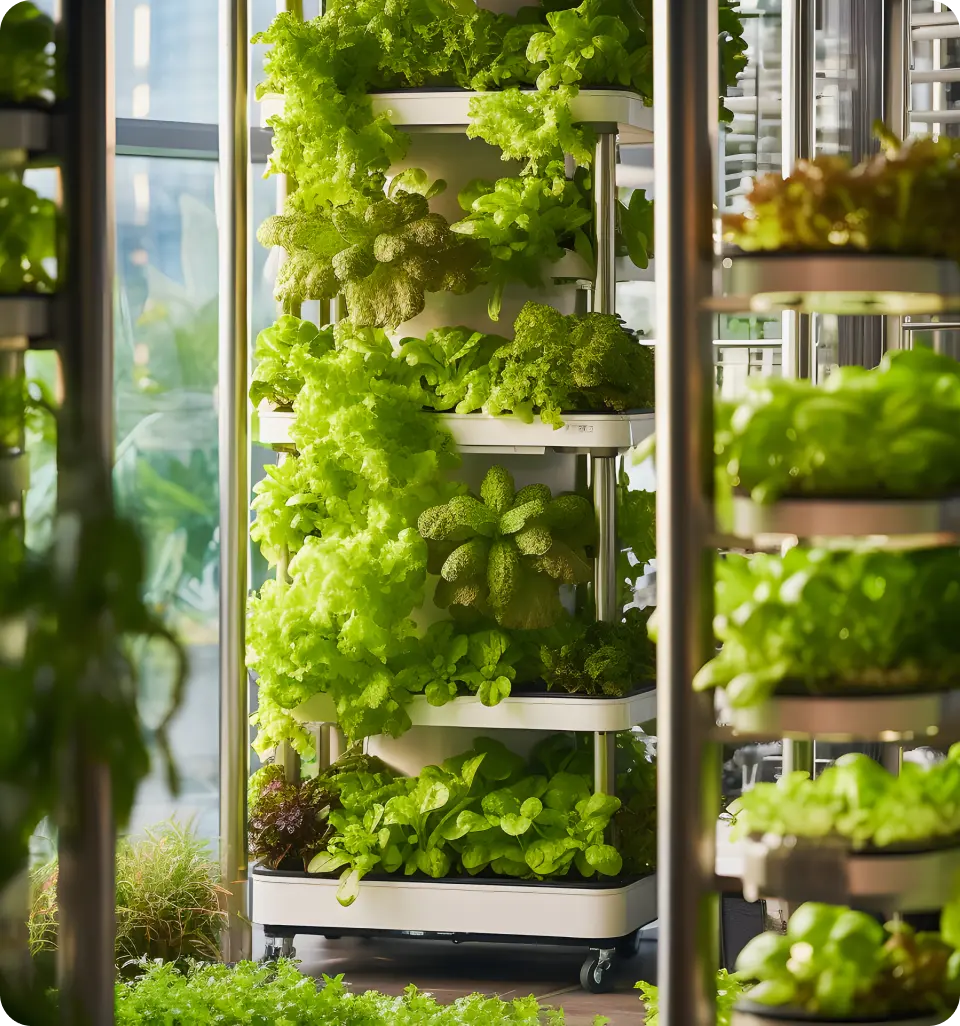
Advanced Hydroponic Features: The Nutraponics Advantage
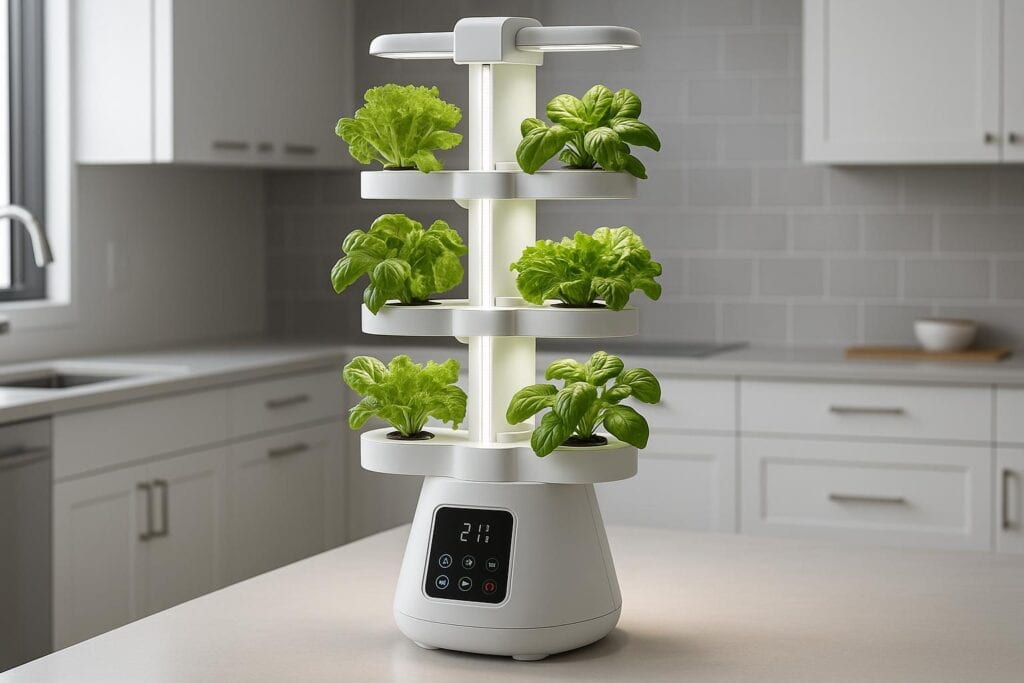 Nutraponics systems combine advanced automation with user-friendly design
Nutraponics systems combine advanced automation with user-friendly designAutomated Monitoring and Control
Modern hydroponic systems like those from Nutraponics incorporate advanced automation features that make growing easier and more successful:
Smart Sensors:
- pH monitoring: Continuous tracking with automatic alerts
- Nutrient concentration: Real-time EC/TDS measurements
- Water temperature: Optimal root zone temperature maintenance
- Water level: Automatic refill notifications and controls
Automated Controls:
- Nutrient dosing: Precise nutrient delivery based on plant needs
- pH adjustment: Automatic pH correction systems
- Lighting control: Programmable LED systems with optimal spectrums
- Environmental management: Temperature, humidity, and air circulation
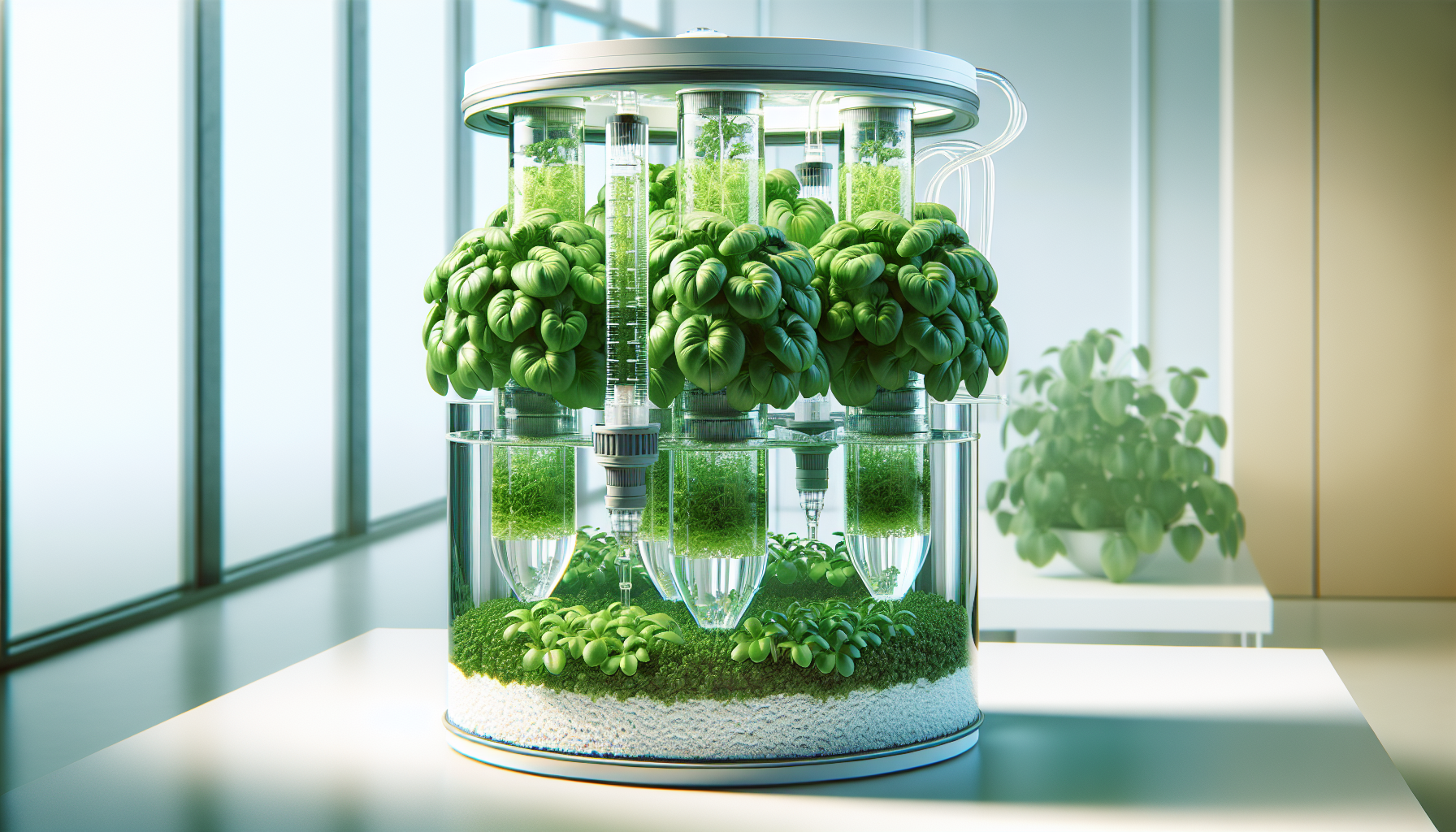
Modular and Scalable Design
Professional hydroponic systems offer expandability and customization:
Modular Benefits:
- Start small and expand as you gain experience
- Add growing capacity without replacing entire system
- Customize for different plant types and growing methods
- Easy maintenance and component replacement
Scalability Features:
- Vertical expansion: Add growing levels as needed
- Horizontal growth: Connect multiple units
- Capacity increases: From 48 to 100+ plant sites
- System integration: Combine different growing methods
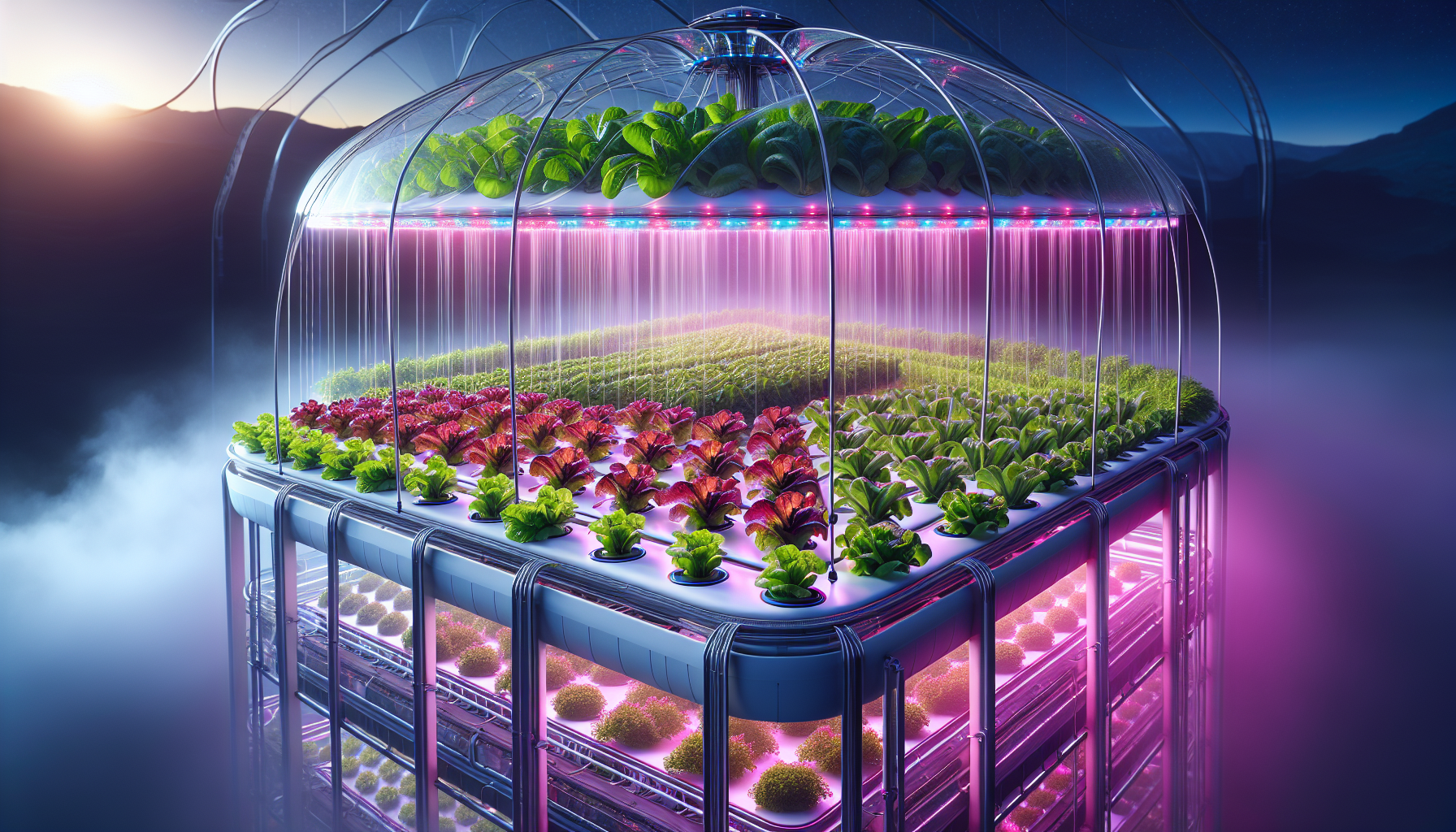
Professional-Grade Components
High-end systems like Nutraponics towers include commercial-quality components:
Advanced Pumps and Circulation:
- Variable speed pumps for precise flow control
- Redundant systems for reliability
- Energy-efficient operation
- Quiet operation for indoor use
Precision Monitoring:
- Laboratory-grade sensors for accuracy
- Data logging and trend analysis
- Remote monitoring capabilities
- Predictive maintenance alerts
Optimized Growing Environment:
- Full-spectrum LED lighting with programmable controls
- Climate control integration
- Air circulation and filtration systems
- Sterile growing conditions
Ready to Experience Advanced Hydroponics?
Discover how Nutraponics systems make hydroponic growing easier and more productive than ever before. From beginner-friendly units to professional-grade towers, find the perfect system for your needs.
Conclusion
Hydroponic systems represent the future of sustainable, efficient growing, offering unprecedented control over plant nutrition and environment. Whether you’re interested in growing fresh herbs on your kitchen counter or establishing a productive home garden, hydroponics provides the tools and techniques to achieve remarkable results.
The key to hydroponic success lies in understanding the fundamental principles: providing plants with optimal nutrition, maintaining proper environmental conditions, and monitoring system performance. With modern automated systems like those offered by Nutraponics, much of the complexity is handled automatically, allowing you to focus on enjoying the process and harvesting fresh, nutritious produce year-round.
As you begin your hydroponic journey, remember that every expert was once a beginner. Start with simple systems and easy-to-grow plants, learn from each growing cycle, and gradually expand your knowledge and capabilities. The investment in time and equipment will reward you with faster growth, higher yields, and the satisfaction of growing your own fresh, healthy food using cutting-edge technology.
Ready to start your hydroponic adventure? Explore Nutraponics’ range of automated hydroponic systems designed to make growing easier, more productive, and more enjoyable than ever before. From beginner-friendly units to professional-grade towers, there’s a perfect system waiting to transform your growing experience.