Sitewide Sale: Use code Get5Nutra for 5% OFF all products. FREE shipping & 30-Days Hassle-Free ReturnsShop Now
Looking to grow plants more efficiently with a Hydroponic Gardening Kit? This guide will show you how to set up a system that feeds nutrients straight to plant roots, enabling faster growth without soil, regardless of the season. We’ll cover the fundamentals, the construction of your hydroponic garden, and the secrets to a plentiful harvest. Dive into the world of hydroponics with us and turn your green aspirations into abundant greens.
Hydroponics is a soilless method of plant cultivation that delivers nutrients directly to plants using a nutrient-rich water solution, which can result in faster and healthier plant growth.
Creating a hydroponic garden requires a setup of specialized equipment and growing mediums, careful management of nutrient solutions, pH balance, and grow lights, with attention to proper aeration and prevention of algae growth.
Hydroponic Gardening Kit systems can face challenges such as higher initial costs, the complexity of setups, and maintaining a controlled environment, but offer benefits like year-round harvesting, a variety of crop cultivation options, and environmentally friendly growing conditions.

Hydroponics, a term coined by William Frederick Gericke, is a method of cultivating plants using nutrient-rich solutions and inert growing media, bypassing soil needs. If you’re wondering about its origins, historical references to hydroponic systems date back to the Hanging Gardens of Babylon and the publication ‘Sylva Sylvarum’ in 1626. So, you see, the concept of soilless cultivation isn’t entirely new.
A hydroponic system primarily comprises:
A water reservoir filled with oxygenated, nutrient-rich water
This setup sidesteps the conventional use of soil by directly delivering essential nutrients to the plants
These innovative hydroponics systems promote efficient and healthier plant growth
Challenges include higher initial costs, complex setups, and the need for diligent nutrient and pH balance control.
Hydroponic Gardening Kit systems stand out due to their unique equipment and growing mediums. Instead of soil, hydroponics uses mediums like Rockwool and coco coir, which provide support to plant roots and facilitate nutrient uptake. Hydroponic-specific equipment like channels and grow trays are engineered to ensure proper drainage and nutrient delivery.
At the core of hydroponic systems is the nutrient solution reservoir. This reservoir contains a blend of water and vital micronutrients and macronutrients, eliminating the requirement for nutrient-dense soil. Another distinctive feature is the supply of dissolved oxygen to plant roots through methods like air stones or the creation of an air gap in certain passive systems. Thanks to this direct delivery of nutrient solutions and proper oxygenation, plants in hydroponic systems experience consistent nutrient access and efficient uptake. This leads to faster and larger growth compared to their soil-grown counterparts.
What underpins the efficient growth of plants in hydroponic systems? The answer lies in the optimal nutrient solution flow rate and proper oxygenation. An ideal flow rate enhances root length, surface area, and volume, improving the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients. Higher flow rates result in more compact roots, increasing their mechanical strength.
Shallow troughs or tray systems like those used in the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) provide plants with constant access to adequate water, air, and nutrients, stimulating healthy root development. Keeping oxygen levels sufficient in water is vital when growing multiple plants with different root lengths in the same container. Moreover, the intensity of grow lights directly influences critical aspects of plant growth such as food production, stem length, leaf color, and flowering.

Ready to embark on your hydroponic gardening journey? It’s an exciting and rewarding venture. The first step is to decide whether to purchase a hydroponic Gardening kit or build your system. This decision depends on your personal needs and budget, as kits can sometimes be pricier. For beginners, a cost-effective start can be a bubbler hydroponic system, which is simple to set up and maintain.
Assembling a basic hydroponic system requires the following items:
Mesh pots
Nutrient solution
Aquarium air pump
Air stones
Air hose
The aeration system is installed by running the airline through the container, attaching air stones, and following package instructions to prevent contamination.
Selecting an appropriate hydroponic Gardening Kit system is a vital decision, hinging on various factors such as your gardening know-how, budget, and available space. Some popular systems for beginners are the nutrient film technique (NFT) and deep water culture systems. One specific type of DWC system is the ebb and flow deep water culture system, which is particularly suitable for a wide range of crops and is versatile. The ebb and flow system is a popular choice among hydroponic enthusiasts due to its adaptability.
If you’re more experienced, you might consider more complex systems like NFT or aeroponic systems. Aeroponic systems provide rapid plant growth but require careful monitoring and knowledge, making them a more complex option for advanced hydroponic gardeners. The design of your hydroponic system is customizable, allowing for expansion or modification to suit your needs and preferences. If you’re working with limited space, vertical systems like NFT or tower gardens are an efficient choice.
After settling on the most suitable hydroponic system, you can start putting your setup together. Here are the steps to follow:
Mount grow trays, channels, or tables securely to provide a raised surface that allows proper drainage and overflow management.
Place the water reservoir directly below the tray setup for a seamless flow of the nutrient solution.
Cut out holes in the container lid to accommodate mesh pots that will house the plants.
Before planting, prepare the containers by:
Adding and moistening the growing medium, such as perlite or coconut coir
Plant your seedlings carefully, ensuring roots are well-positioned within the growing medium and leaving appropriate space between each plant
Mix the nutrient solution with precise measurements according to the directions, adjusting the pH to the correct level for the plants you’re growing
Finally, connect the system to a water and potentially an air pump, ensuring the circulation and oxygenation meet the needs of your specific hydroponic setup.
The nutrient solution is a vital element of hydroponic gardening. It replaces the nutritional role of soil in hydroponics through fertilizers or nutrient mixes that supply essential micronutrients and macronutrients. Nutrient levels should be monitored daily, with adjustments and additions made every few days based on plant uptake and water dilution.
Additionally, here are some maintenance tips for your hydroponic system:
Every other week, the nutrient solution should be entirely replaced to prevent the buildup of excess nutrients that can stunt plant growth.
In case of imbalances, the system can be flushed with distilled water.
If water hardness or high mineral content presents an issue, a reverse osmosis system can be used to improve water quality for nutrient dissolution and plant absorption.
For beginners, using liquid nutrient concentrates is recommended as they are easier to mix and manage for precise control over nutrient levels.
Another fundamental aspect of hydroponics is maintaining the right pH levels. It ensures healthy plant growth and effective nutrient absorption. Improper pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which may manifest as symptoms such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth.
To monitor pH levels, you can use digital pH meters, liquid test kits, or pH test strips, with digital meters offering the highest accuracy. The pH level can be adjusted using ‘pH up’ or ‘pH down’ products, aiming for a slightly acidic level between 5.5 and 6.0 for most crops.
Like any form of gardening, hydroponics isn’t without its challenges. One of the most common problems is the growth of algae. Preventing light from reaching the nutrient solution is essential to inhibit the growth of algae. Maintaining high levels of dissolved oxygen in the nutrient solution helps prevent the development of harmful microbes like algae.
Regular cleaning of the hydroponic system, including brushing and flushing, is crucial for removing algae and restarting with a clean nutrient solution. Algae can elevate pH levels during the day, and bacteria from root diseases can cause sudden pH drops, thus regular pH monitoring and control are vital.
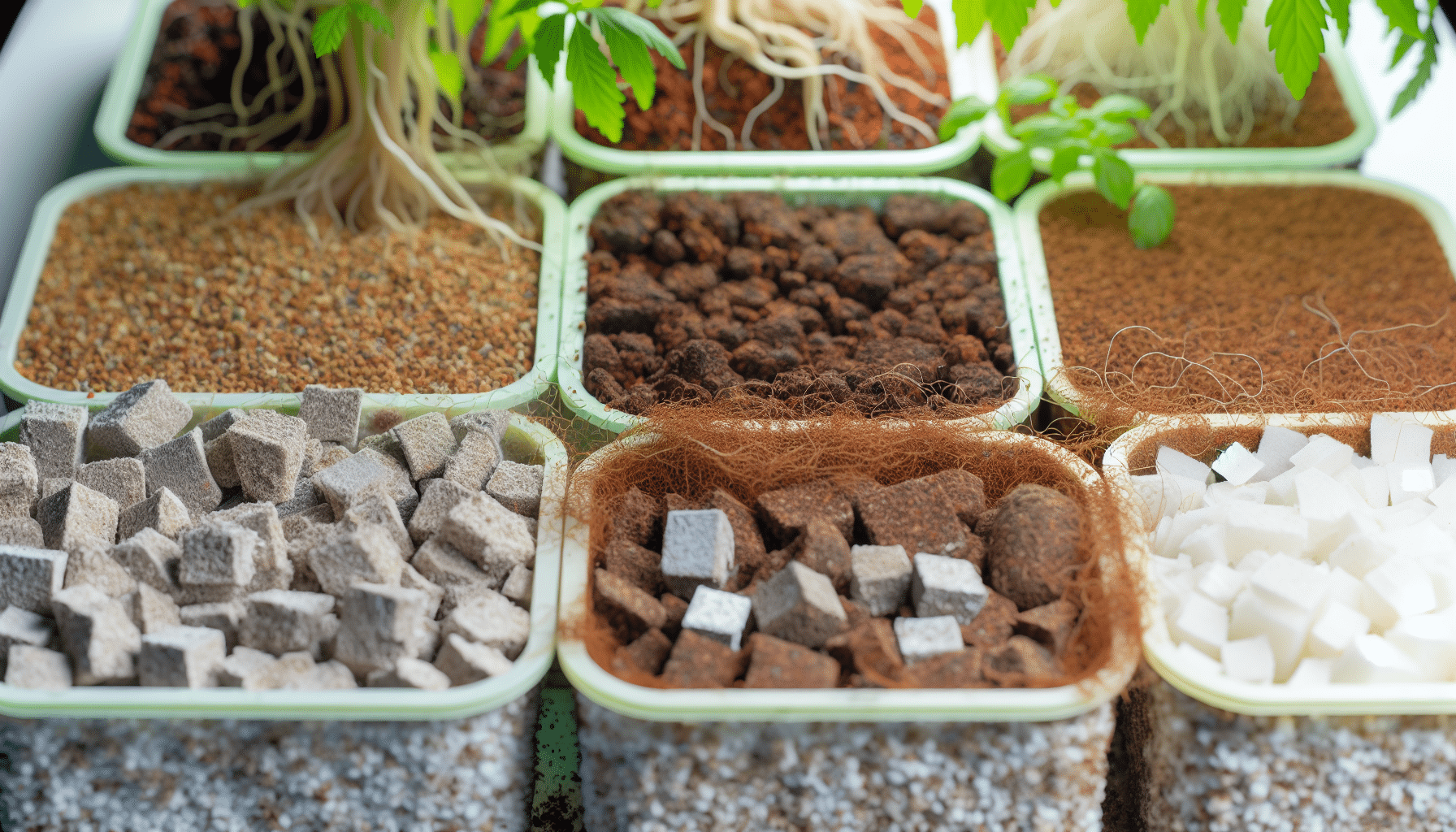

In hydroponics, the soil is replaced by a growing medium, which plays a pivotal role in the growth of plants. It provides stability to plant roots while ensuring ample oxygenation. Rockwool and coco coir are examples of such mediums used in hydroponics. They offer a sterile environment for root development and nutrient absorption.
Different plants have preferences for certain hydroponic growing mediums. Some thrive in mediums with higher water retention, while others prefer well-draining mediums. Factors such as cost, availability, sustainability, reusability, and pH stability should be considered when selecting a hydroponic growing medium.
Selecting an appropriate hydroponic medium is crucial for providing adequate root support and oxygenation, both essential for ideal plant growth. Rockwool is known for its water retention and aeration, contributing to robust root support and oxygen supply. Coconut coir, on the other hand, provides good water retention and aeration, contributing to stable root development.
Each hydroponic medium offers distinct advantages. Understanding these can help gardeners improve plant growth by optimizing root support and oxygenation. For instance, perlite offers excellent aeration and drainage, ensuring the roots receive sufficient oxygen. While vermiculite retains a high amount of water, it needs to be mixed with other mediums to improve drainage and oxygen flow to roots.
After deciding on the most suitable medium, the subsequent step involves transitioning plants to the chosen hydroponic medium. This process involves hardening, which gradually adapts plants to hydroponic environmental conditions, often starting in a greenhouse. To ensure high humidity levels and a smooth transition, a mini greenhouse can be created using a transparent plastic dome.
Plants need to be slowly adapted to lower relative humidity and increased light levels to encourage growth suitable for the hydroponic system. Once plants have acclimatized with new leaves and roots developed, they can safely be transferred to the final hydroponic setup, with close monitoring for any stress.
Artificial lighting, which substitutes for the natural sunlight that plants typically receive, is a necessary component of indoor hydroponic gardening. While window light can suffice for small hydroponic gardens, larger setups require additional artificial light sources to provide sufficient light for plant growth.
Some popular types of grow lights include:
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, such as high-pressure sodium and metal halide bulbs, which are efficient and produce high luminosity. They are suitable for different growth stages and commercial growers.
Fluorescent lights, including T5 High output bulbs and Compact Fluorescent Lights (CFLs), which are energy-efficient and produce minimal heat.
LED grow lights, which are favored for their longevity, energy efficiency, low heat emission, and ability to be tailored to provide specific light wavelengths.
Adjusting the light spectrum and intensity is key to maximizing photosynthetic efficiency and promoting plant growth in hydroponics. The visible light spectrum for plants ranges from 400 nm (violet) to 780 nm (red), and this range includes different wavelengths that influence various stages of plant growth. Different plant species and growth stages may require varying light spectrums, which can range from red/blue to full-spectrum lighting to match the natural conditions plants would experience outdoors.
Full-spectrum LED lights are popular in hydroponics as they can offer a wide range of wavelengths, including UV and Far Red, and are customizable for specific plant growth stages. Additionally, to provide consistent exposure to light, grow lights in a hydroponic garden should be set on a timer, typically for 12 to 16 hours per day.
The correct distance for grow lights above plants is crucial to avoid leaf burn and ensure efficient energy use.
When choosing lighting for hydroponic systems, energy efficiency is a paramount consideration. LED grow lights, fluorescent bulbs, and HID types such as metal halide and high-pressure sodium bulbs are energy-efficient options that are commonly used. LED grow lights stand out as a leading choice due to their long lifespan, energy efficiency, and minimal heat production.
Applying reflective materials to the walls and ceilings of grow rooms, or painting them white, can significantly increase the energy efficiency of hydroponic lighting by maximizing light exposure to the plants. However, fluorescent bulbs, though energy-saving, contain mercury and require careful disposal or recycling to avoid environmental harm.
Hydroponic plants progress through a lifecycle that spans from seedling to harvest. Seeds for hydroponic gardens should be started separately and then transplanted into the hydroponic system after germination to ensure proper development. To avoid overwatering and root rot during the early growth phase, a mist spray can be used to keep the growing medium adequately moist without over-saturation.
One of the advantages of hydroponic gardening is:
the ability to harvest crops all year round
resulting in predictable yields
environmental benefits such as decreased greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
The process of germinating seeds for hydroponic Gardening includes the following steps:
Soak the seeds in water for 6-12 hours to soften the seed coat and encourage water uptake.
Provide warmth, typically between 68ºF and 77ºF (20ºC and 25ºC), and humidity to sprout the seeds.
Place the soaked seeds in Rockwool seed cubes.
Hand-water the seed cubes to support proper germination and early growth.
Timers can be used to automate grow lights, providing consistent light exposure each day which is crucial for even and strong growth during germination. This step sets the stage for the plant’s development and growth through its lifecycle.
After germination, the plants enter the vegetative phase. During this phase, optimal environmental conditions are crucial, including maintaining appropriate water levels for root aeration and ensuring temperature ranges between 20°C and 30°C. Adjusting lighting for plant growth stages is also important. For instance, HID grow lights with Metal Halide are used for vegetative growth and High-Pressure Sodium for flowering.
As the plant matures, it transitions from the vegetative to the flowering stage. This transition is achieved by changing light cycles to 12 hours on and 12 hours off for photoperiod plants while sustaining consistent light for autoflowering varieties. Throughout these stages, it’s crucial to tailor lighting wavelengths using red light spectrum for encouraging photosynthesis and flowering and far-red to initiate plant responses leading to stretching or in some cases increased fruit yield.
The final stage in the lifecycle of hydroponic plants is the harvest. Plants should be harvested when they reach the desired maturity level, which is critical for maximizing plant health and ensuring continuous yields. Hydroponic plants can yield 2-10 times more produce at half the time and space than conventional soil-based plants when harvested properly.
During harvesting, plants should be handled carefully using clean instruments for cutting to avoid damage to the roots and minimize the risk of disease. For the best flavor and texture, harvest leafy greens and herbs in the morning when the water content is highest. For fruiting crops, wait until they are fully ripe since they do not continue to ripen once picked.
Despite its numerous benefits, hydroponics is not devoid of challenges. Like any form of cultivation, hydroponic systems may encounter diseases such as powdery mildew, downy mildew, and root rots, which can significantly affect plant health. Additionally, hydroponic gardeners need to address issues such as pests by employing strategies to manage common pests like thrips, mites, aphids, and whiteflies.
Another challenge is ensuring successful germination in hydroponic systems. Common mistakes to avoid include:
Improper timing
Incorrect growing medium selection
Inadequate light or heat
Improper watering
Despite these challenges, hydroponics leads to purer food crops, free from common soil-related contaminants like pesticides and herbicides, and prevents issues such as fertilizer runoff.
Identifying and managing plant diseases is an essential aspect of maintaining a thriving hydroponic garden. Early recognition of symptoms is critical in managing plant health. Common diseases like powdery mildew and downy mildew appear as white or grayish spots on leaves. Pests like spider mites, thrips, aphids, and whiteflies show distinct signs like webbing and discolored leaves.
To prevent the growth of pathogens in hydroponic systems, it’s essential to:
Clean the roots and remove residues such as sucrose or gel media
In some cases, it may be beneficial to immerse plants in a fungicide solution to prevent fungal infections
In the case of algae issues, hydrogen peroxide can be used as a treatment method.
Sustaining a controlled environment in hydroponics entails regulating:
Temperature
Humidity
Air circulation
Light
Ideal temperatures should be maintained between 68 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit to prevent stunted plant growth. Regulating the grow room’s humidity between 40 to 60 percent also helps stimulate plant growth and reduces disease risk.
Aeration methods, including air pumps and air stones, supply the nutrient solution with sufficient dissolved oxygen, vital for root health and efficient plant growth. Consistent airflow in the grow room provides the plants with ample carbon dioxide, which is beneficial for faster growth. Controlled lighting is pivotal for managing the photoperiod, which influences plant growth by replicating natural outdoor light cycles.
The ability to cultivate a variety of crops is one of the thrilling aspects of hydroponic gardening. Some crops that are ideal for hydroponic cultivation include:
Leafy greens such as lettuces, due to their rapid growth and high nutrient uptake efficiency in controlled environments
Fruits such as strawberries and tomatoes
Vegetables such as peppers and cucumbers
Herbs such as basil and mint
Hydroponic gardening offers a wide range of possibilities to grow plants, including hydroponically grown plants and different types of plants as plants grow in this method.
If you’re a beginner, there are certain plants that are easier to grow hydroponically. Some of the easiest plants to cultivate are:
Lettuce
Spinach
Mizuna
Basil, including unique varieties like lemon basil and red basils
These plants are highly suitable for beginner hydroponic gardeners due to their ease of cultivation.
You can also experiment with the following plants:
Bok Choi, known for its swift growth cycle
Oak Leaf lettuce, for its distinctive appearance
Fruit-bearing plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, radishes, and bell peppers, which are relatively easy to grow for beginners and offer a rewarding yield
Strawberry plants, for a sweet reward from your hydroponic ventures.
For the more adventurous gardeners, hydroponics offers an opportunity to grow exotic plants. Cultivating exotic plants like wasabi and vanilla orchids adds a layer of excitement beyond the basics of hydroponic gardening. These high-value exotic plants require specific environmental conditions, such as water quality, temperature, and humidity.
Hydroponic cultivation of saffron demands advanced skills and precise control over the growing environment.
In conclusion, hydroponic gardening offers a sustainable and efficient way to grow plants year-round. Whether you’re a beginner starting with easy-to-grow lettuce or an experienced gardener trying your hand at exotic saffron, hydroponics offers endless possibilities. With the right system, growing medium, lighting, and nutrient solution, you can cultivate a thriving hydroponic garden. Now that you have a comprehensive guide at your fingertips, are you ready to embark on your hydroponic gardening journey?
You can grow a variety of plants hydroponically, including leaf lettuce, tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, strawberries, watercress, celery, and herbs. The design of the system should consider how each crop is supported in the nutrient solution.
Hydroponic gardening is a method of growing plants without soil, using a water-based nutrient solution or growing media like vermiculite or coconut coir. It allows for year-round indoor cultivation of various edible plants.
The main disadvantages of hydroponic farming include limited nutrient variability, initial setup costs, and susceptibility to power outages. It is important to carefully consider these factors before starting a hydroponic farm.
To start a hydroponic garden, follow these 7 steps: choose plants and start seeds, decide on a system, select a light source, choose a grow medium, purchase nutrients and supplements, get a pH meter and adjust pH, then mix nutrients and start the system.
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using a water-based nutrient solution. It allows for year-round indoor cultivation and is used by small farmers, hobbyists, and commercial enterprises.
Grow 100 planting sites, monitor ph levels, water temperature, water levels, and control light and water cycles.
© Copyright 2024 Nutraponics. All Rights Reserved.